Learn Cardiovascular system basics | MPO training 3
Learn Cardiovascular system basics with this simple and clear guide for Medical Promotion Officer (MPO) aspirants. This article explains how the heart and blood vessels work together.
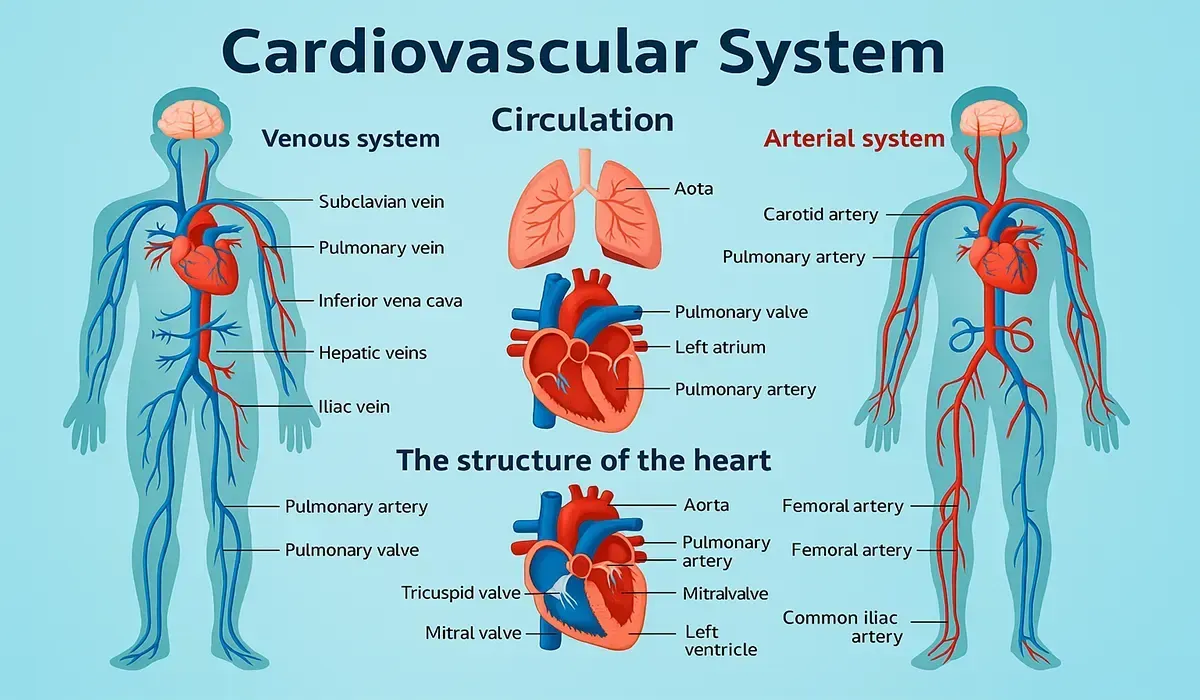
Diagram: Cardiovascular system diagram
It uses real-world examples and avoids medical jargon. Even if you’re new, you’ll understand quickly. Build confidence and grow your career step by step.
Table of content: Learn Cardiovascular system basics
What you will get in this blog post-
- Learn Cardiovascular system basics
- Blood and its composition
- Plasma, plasma proteins and Serum
- Blood cells
- General Properties of Blood
- Blood vessels: Types
- Blood Circulation
- Blood Pressure
- Blood Pressure for Adult
- Heart
- Effects on Heart
- Important Definitions
- Hypertension
- Common Diseases
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Learn Cardiovascular system basics
To learn cardiovascular system basics, start with how the heart pumps blood throughout your body. Understand the role of arteries, veins, and capillaries in blood circulation. This basic knowledge is essential for every Medical Promotion Officer (MPO). It helps you explain drug actions to doctors clearly. Begin with the simple structure and grow from there.
Here you can learn - Contents:
- Description of the Cardiovascular System.
- Physiology of the Cardiovascular System.
- Monitoring and Diagnostic Techniques of the Cardiovascular System.
Cardiovascular System
Cardiovascular system is a transport system that transports important
substances
around the body.
Components of the cardiovascular system are:
- Heart
- Blood
- Blood vessels
Blood and its composition
Blood is a suspension of cells in plasma.
- Blood = Cell + Plasma.
Composition of Blood-
Diagram: Blood vessel diagram
A. Cellular substance (cell):
- Erythrocytes or RBC (Red Blood Corpuscles)
- Leukocytes or WBC (White Blood Corpuscles)
- Platelets or Thrombocytes
B. Liquid substance (Plasma):
- Inorganic substance.
- Organic substance (Proteins, Non protein nitrogenous substances, Fats, Carbohydrates and other).
Plasma, plasma proteins and Serum
Plasma is the liquid part of blood, which is a solution of protein and
salts.
- Plasma = Serum + Coagulation proteins and factors.
Plasma Proteins:
- Albumin
- Globulin
- Fibrinogen
Serum
Serum is the fluid or the watery portion that remains after blood
coagulation.
- Serum = Plasma - coagulation proteins and factors.
Blood cells
Erythrocytes/RBC:
These are nucleus less cells containing hemoglobin and carry oxygen from
the lung to all the tissues where it is exchanged for carbon dioxide.
Haemoglobin
It is the red pigment of the blood present in the RBC. Haemoglobin binds
with oxygen and is converted to oxyhaemoglobin in the lung.
It is composed of two parts:
- Haemoglobin = Haem (red pigment) + Globin (protein).
Leukocytes/WBC:
Leukocytes are defensive substances of the body, which defend against
microorganisms that enter the body from the environment.
There are two types of WBC:
1) Granular:
- Neutrophil
- Basophil
- Eosinophil
2) Agranular:
Diagram: thrombocytes platelets diagram
General Properties of Blood
Blood volume is an average of 56 litres.
Blood pH value is 7.367.45.
Blood temperature is average 36-38 °C.
Viscosity of blood is 4.5 times more than that of water.
Functions of the Blood:
- Transport function.
- Regulation function.
- Defensive function.
Blood vessels: Types
The blood vessels are hollow tubes that carry the blood to and from the
tissues.
There are three types of blood vessels:
- Artery
- Vein
- Capillary
Diagram: types of blood vessels diagram
Artery: Carries oxygenated blood from heart to all over the body.
Vein: Carries deoxygenated blood from all over the body to heart.
Capillary: Capillary are fine vessels that link or or junction the
small arterioles and arterioles and smallest venules.
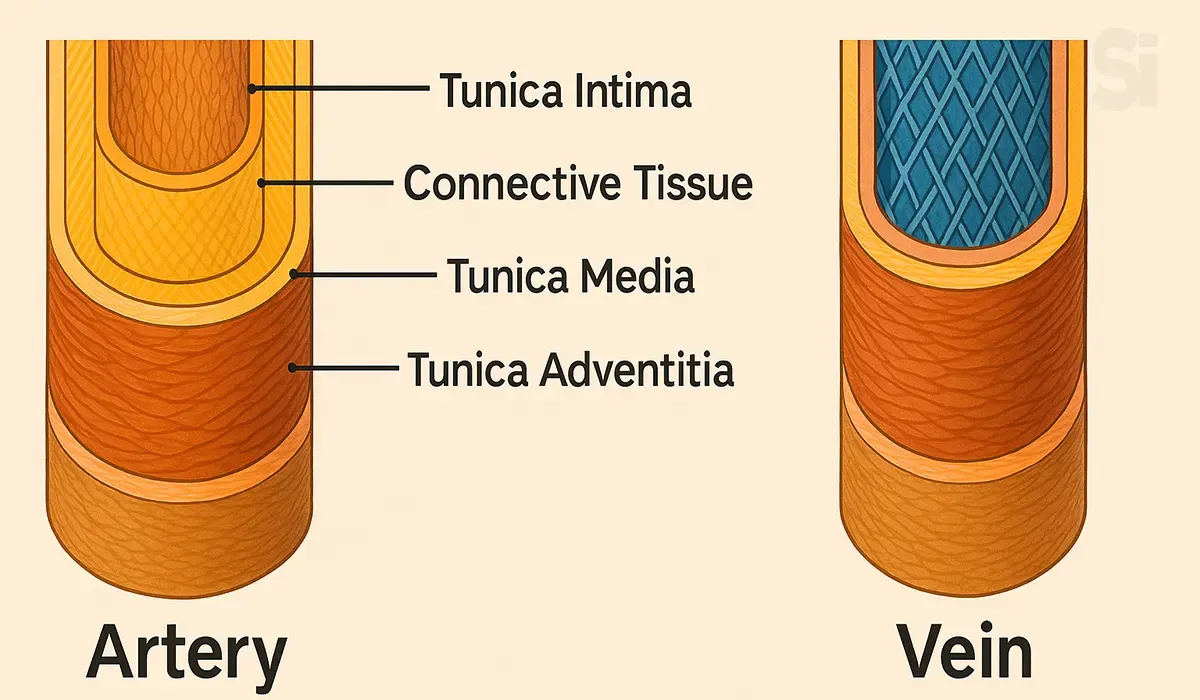
There are three layers in the blood vessels:
Tunica Intima: A thin layer of flat epithelial cells. The innermost
layer of blood vessels.
Tunica Media: The middle layer composed of smooth muscle fibers and
elastic fibers.
Tunica Adventitia: 👇
Diagram: Tunica Adventitia diagram
Blood Circulation
Circulation is a process of blood flow through a closed system of vessels.
- Systemic Circulation
- Pulmonary Circulation
- Coronary Circulation
- Hepatic portal Circulation
Diagram: Blood Circulation diagram
Importance of circulation:
- To supply oxygen, nutrition, vitamins to the tissues.
- To carry different metabolic waste products and carbon dioxide from tissue.
- To prevent intravascular coagulation of blood.
- To maintain an environment for cellular function.
Factors of maintaining Circulation:
- Pumping action of heart.
- Elastic recoil of arteries.
- Pressure gradient.
- Respiration.
- Muscular exercise.
Blood Pressure
Blood Pressure is the pressure lateral exerted by the flowing blood on
the wall of blood vessels.
Systolic Pressure: The pressure exerted by the blood on the
blood vessels during contraction of the heart. It is 120 Hg for a
normal person.
Diagram: blood pressure diagram
Diastolic Pressure: The pressure exerted by the blood on the
blood vessels during relaxation of the heart. It is 80 Hg for a normal
person.
Blood Pressure for Adult
| Category | Systolic (mm Hg) | Diastolic (mm Hg) |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | <130 | <85 |
| High Normal | 130-139 | 85-89 |
| Hypertension | Systolic (mm Hg) | Diastolic (mm Hg) |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | 140-159 | 90-99 |
| Moderate | 160-179 | 100-109 |
| Severe | 180-209 | 110-119 |
| Very Severe | 210 or more | 120 or more |
Heart
Heart is the central blood-pumping organ of the body. It receives and
pumps blood from and to all over the body. It is a hollow muscular organ.
A. Heart Chambers:
The Heart has four chambers:
Diagrame: Heart four chambers
* Receiving Chamber
- Right atrium
- Left atrium
* Distributing Chamber
- Right ventricle
- Left ventricle
Diagrame: Heart chambers diagram
B. Heart Muscles:
The Pericardium: Outermost layer surrounding the heart.
The Myocardium: Middle muscular layer of the heart.
The Endocardium: The Innermost layer of the heart.
Diagram: Heart Muscles diagram
C. Valves of Heart
Valve is a membranous structure that temporarily closes in order to permit
flow of fluid in one direction.
Diagram: Valves of Heart diagram
There are four types of valves in the heart:
- Tricuspid or right atrio-ventricular valve.
- Mitral valve or Left atrio-ventricular valve.
- Pulmonary valve.
- Aortic valve.
D. Heart Conduction System
Special tissues responsible for initiation and propagation of cardiac
impulses.
Diagram: Heart Conduction System diagram
These are:
- Sinoatrial node.
- The Internodal pathway.
- AtrioVentricular node.
- The AtrioVentricular bundle/Bundle of His.
- The left and right bundles of AV brunch.
- The Purkinje fibers.
E. Heart Contraction nerve influences
There are two sets of nerves that influence the rate of contraction of
the heart:
- The Vagus nerve which slows the rate and lessens the strength of the beat.
- The Sympathetic nerves which quickens and increase the strength of the beat.
Diagram: Heart Contraction nerve influences diagram
Effects on Heart
A. Effects on Heart: Potassium-
Excess potassium in the extracellular fluid causes-
- The heart becomes extremely dilated.
- Flaccid and slower heart rate.
B. Effects on Heart: Calcium
Excess calcium ion causes-
- Increased Contraction of heart and blood vessels.
C. Effects on Heart : Sodium
Excess Sodium ion causes-
- Depression of cardiac function.
- Dilate and flaccid the heart.
D. Effects on Heart: Adrenaline
Adrenaline increase the rate and force of contraction as it-
- Stimulates S A Node.
- Increases conductivity, contractility and automaticity.
Important Definitions
Heart Rate: The number of heart beats per minute is called heart
rate.
Normal Heart rate-
- Adult: 60-90/minute
- Average: 72/minute
Cardiac Output: The amount of blood the heart pumps through the
circulatory system in a minute.
Usually, an adult heart pumps about 5 liters of blood per minute at rest.
But when you run or exercise, your heart may pump 3-4 times that much to
make sure your body gets enough oxygen and fuel.
Tachycardia: The term tachycardia means a faster heart rate than
the normal.
Usually above 100 beats/minute) is called tachycardia.
Bradycardia: The term bradycardia means slower heart rate than the
normal physiological limit.
Usually below 60 beats/minutes is called bradycardia.
Hypertension
Hypertension is a clinical condition in which the patient has a higher
blood pressure than that judged to the normal.
Diagram: Hypertension diagram
Etiology:
- Actual cause of hypertension is known.
Risk Factor:
- Generic
- Smoking
- High lipid content
- Overweight
Hypertension Types
Two types:
Essential or Primary Hypertension: Hypertension for which no cause
is known is called primary or essential or idiopathic hypertension.
Diagram: Types of Hypertension diagram
Secondary Hypertension: Hypertension for which the cause is known
is called secondary hypertension.
Common Diseases
Anemia: Anemia is a reduction of hemoglobin concentration per unit
of peripheral blood. As a result, Oxygen carrying capacity of blood is
decreased.
Aplastic Anemia: Anemia which is due bone marrow depletion, is
called Aplastic anemia.
Leukemia: It is a disease due to abnormal increase in WBC.
Endocarditis: Inflammation of Endocardium is called Endocarditis
Atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis is a disease in which the inside
of an artery narrows due to the buildup of plaque.
Ischemic Heart Disease: Coronary artery disease (CAD), also known
as Coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD) or simply
heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle
due to build-up of plaque (atherosclerosis) in the arteries of the heart.
It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases.
Myocardial Infarction: A heart attack occurs when one of the
heart's coronary arteries is blocked suddenly or has extremely slow blood
flow. A heart attack also is called a myocardial infarction.
Angina pectoris: Angina pectoris is the medical term for chest pain
or discomfort due to coronary heart disease.
Arrhythmia: Arrhythmia, also known as cardiac arrhythmia or heart
arrhythmia, is a group of conditions in which the heartbeat is irregular,
too fast, or too slow.
FAQs
Q. What is the full form of RBC?
A. The full form of RBC is Red Blood Corpuscles.
Q. What is the full form of WBC?
A. The full form of WBC is White Blood Corpuscles.
Q. What is another name for Platelets?
A. Another name for Platelets is Thrombocytes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when you learn cardiovascular system basics, you take your first step toward being a smart and confident Medical Promotion Officer (MPO). This topic builds your understanding of how the human body works. It improves your communication with doctors. Simple knowledge leads to strong trust. So keep learning and move ahead with purpose.