Endocrine system for beginners | MPO training 9
Discover the basics of the endocrine system in this simple and
beginner-friendly guide. If you're a future Medical Promotion Officer (MPO),
this article will help you understand how hormones affect the body. The
endocrine system controls growth, metabolism, and many other body functions.
Diagram: Endocrine system
This content is ideal for anyone starting a medical career. You’ll find easy
terms and real-life examples. Learn more in this helpful post on the
endocrine system for beginners. It’s perfect for exam prep and medical
discussions.
Table of contents: Endocrine system for beginners
Find out what you will learn in this article-
Endocrine system for beginners
The endocrine system for beginners is a simple way to learn how your body
uses hormones. It includes glands like the thyroid, pituitary, and adrenal
that release hormones into the blood. These hormones help control energy,
mood, growth, and more.
As a Medical Promotion Officer (MPO), understanding this system is
important when promoting related medicines. This article explains each
gland in plain words so you can remember and apply the knowledge easily.
You’ll find this guide helpful for both job interviews and real-world MPO
work.
What is an Endocrine system?
The endocrine system is a series of glands that produce and secrete
hormones that the body uses for a wide range of functions.
What is an Endocrine gland?
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete
their products, hormones, directly into the blood.
Diagram: Endocrine gland
What are Hormones?
Hormones are secreted in the body by several glands that are essential for
the growth, development, reproduction, etc.
Diagram: Hormone
Hormones are your body's chemical messengers.
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is a small but vital part of the brain. It
controls body temperature, hunger, thirst, emotions, and sleep.
It also links the nervous system to the endocrine system through
the pituitary gland. Without the hypothalamus, the body cannot
maintain balance (homeostasis).
Diagram: Hypothalamus
It plays a major role in hormone production and regulation. Damage to
the hypothalamus can lead to serious health issues like obesity, growth
problems, and emotional imbalances.
Hormones from Hypothalamus
Hypothalamus ➡️ Releasing Factors ⬇️
- Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone
- Oxytocin
- Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone
- Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone
- Vasopressin
- Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone
- Somatostatin
Diagram: Hypothalamus Releasing Factors
Pituitary Gland
Controlled by the hypothalamus/6-m Located at the base of the brain.
Diagram: Pituitary Gland
Pituitary Hormones
Pituitary hormones are produced by the pituitary gland, also called the
"master gland". These hormones control growth, metabolism,
reproduction, and stress responses. Some important pituitary hormones are
growth hormone (GH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
*The gland has two parts: anterior and posterior, each
releasing different hormones. Pituitary hormones work by signaling other
glands to produce their hormones.
Diagram: Pituitary Hormones
Thyroid and Parathyroid Gland
Thyroid Gland
Located below the larynx.
Diagram: Thyroid Gland
Parathyroid Gland
Four located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
Secrete parathyroid hormone.
The major function of the parathyroid glands is to maintain the body's
calcium and phosphate levels.
Diagram: Parathyroid Gland
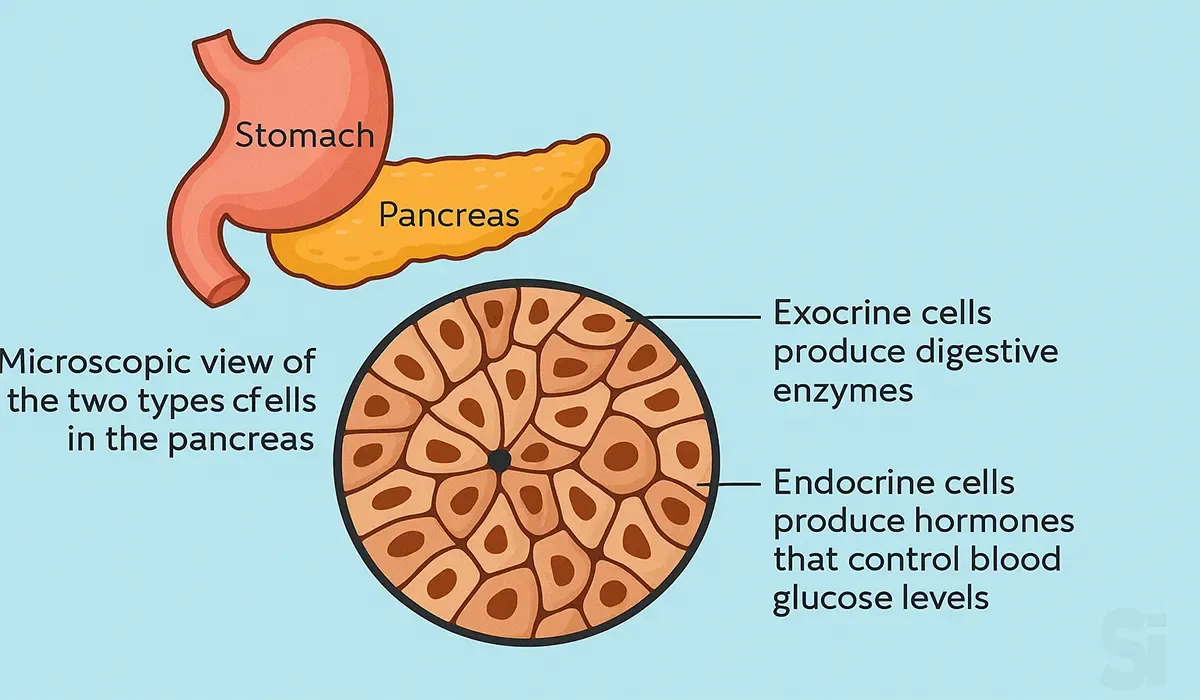
Pancreas
Microscopic view of the two types of cells in the pancreas.
- Exocrine cells produce digestive enzymes.
- Endocrine cells produce hormones that control blood glucose levels.
Diagram: Pancreas
Pancreatic Hormones
Islets of Langerhans secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
- Alpha cell (secretes glucagon)
- Beta cell (secretes insulin)
- Delta cell (secretes somatostatin)
Exocrine pancreas (acinar cells and duct cells).
Diagram: Pancreatic Hormones
Adrenal Gland
The adrenal glands are small glands located above each kidney.
They produce important hormones like cortisol, adrenaline, and
aldosterone. These hormones help control blood pressure, stress
response, metabolism, and salt balance.
Diagram: Adrenal Gland
Each adrenal gland has two parts:
- Adrenal cortex and
- Adrenal medulla
They work together to keep the body healthy during stress and
emergencies.
Adrenal Hormones
Adrenal hormones are chemicals released by the
adrenal glands. They include cortisol (stress hormone),
aldosterone (salt balance hormone), and adrenaline (fight-or-flight
hormone). These hormones help manage stress, blood pressure, immune
responses, and energy metabolism. Proper adrenal hormone function is
vital for survival, especially during emergencies.
Diagram: Adrenal Hormones
Ovarian Hormones
Ovarian hormones are mainly estrogen and progesterone, produced by the
ovaries. These hormones regulate the menstrual cycle,
pregnancy, and female secondary sexual characteristics. Estrogen
supports the growth of the uterine lining, while progesterone prepares
it for pregnancy. Hormonal imbalance can cause fertility problems and
other health issues.
Diagram: Ovarian Hormones
Testes
It releases the hormone testosterone.
The testes are male reproductive glands located in the scrotum.
They produce testosterone and sperm. Testosterone controls male
secondary sexual features like voice deepening and muscle growth. It
also plays a role in mood, energy, and fertility. Healthy testes are
essential for male reproduction and hormonal balance.
Diagram: Testes
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a
group of metabolic disorders which are characterized by a high blood
sugar level over a prolonged period of time.
a) Type I Diabetes Mellitus - results from the pancreas's
failure to produce enough insulin due to loss of beta cells. referred
to as "insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus or "juvenile diabetes".
b) Type II Diabetes Mellitus - begins with insulin resistance,
a condition in which cells fail to respond to insulin properly.
c) Gestational Diabetes Mellitus - occurs when pregnant women
without a previous history of diabetes develop high blood sugar
levels. It is a temporary condition. It resolves after termination of
pregnancy.
What are common diseases of the endocrine system?
Some common diseases of the endocrine system are:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypothyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism
- Addison’s disease and
- Cushing’s syndrome
FAQs
Q) What happens if the endocrine system is not working
properly?
A) Problems in the endocrine system can cause conditions like
diabetes, thyroid diseases, growth disorders, and hormonal
imbalances.
Q) What is the full meaning of DM?
A) The full meaning of DM is Diabetes mellitus.
Q) What is the full meaning of IDDM?
A) The full meaning of IDDM is Insulin-dependent diabetes
mellitus.
Q) Which organs are part of the endocrine system?
A) Key organs of the endocrine system include the
hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands,
pancreas, ovaries and testes.
Q) What are the main glands of the endocrine system?
A) The major glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary
gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries (in
females), and testes (in males).
Q) How many types of diabetes?
A) Diabetes are 3 types, such as Type I Diabetes, Type II
Diabetes and Gestational Diabetes.
Q) How does the endocrine system differ from the nervous
system?
A) The nervous system sends quick electrical signals, while
the endocrine system sends slower, long-lasting hormonal messages
through the blood.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article gives you a clear view of the endocrine
system for beginners. As a future or current Medical Promotion
Officer (MPO), you must understand how the endocrine system works to
promote hormonal drugs properly. This guide helps you connect the
theory with your daily MPO tasks.
You can now explain hormone roles and related conditions with more
confidence. This article also prepares you better for MPO exams and
field interactions. Keep learning and applying this medical
knowledge - it will truly help you in your career.